MonoDense
airt.keras.layers.MonoDense
¤
Bases: Dense
Monotonic counterpart of the regular Dense Layer of tf.keras
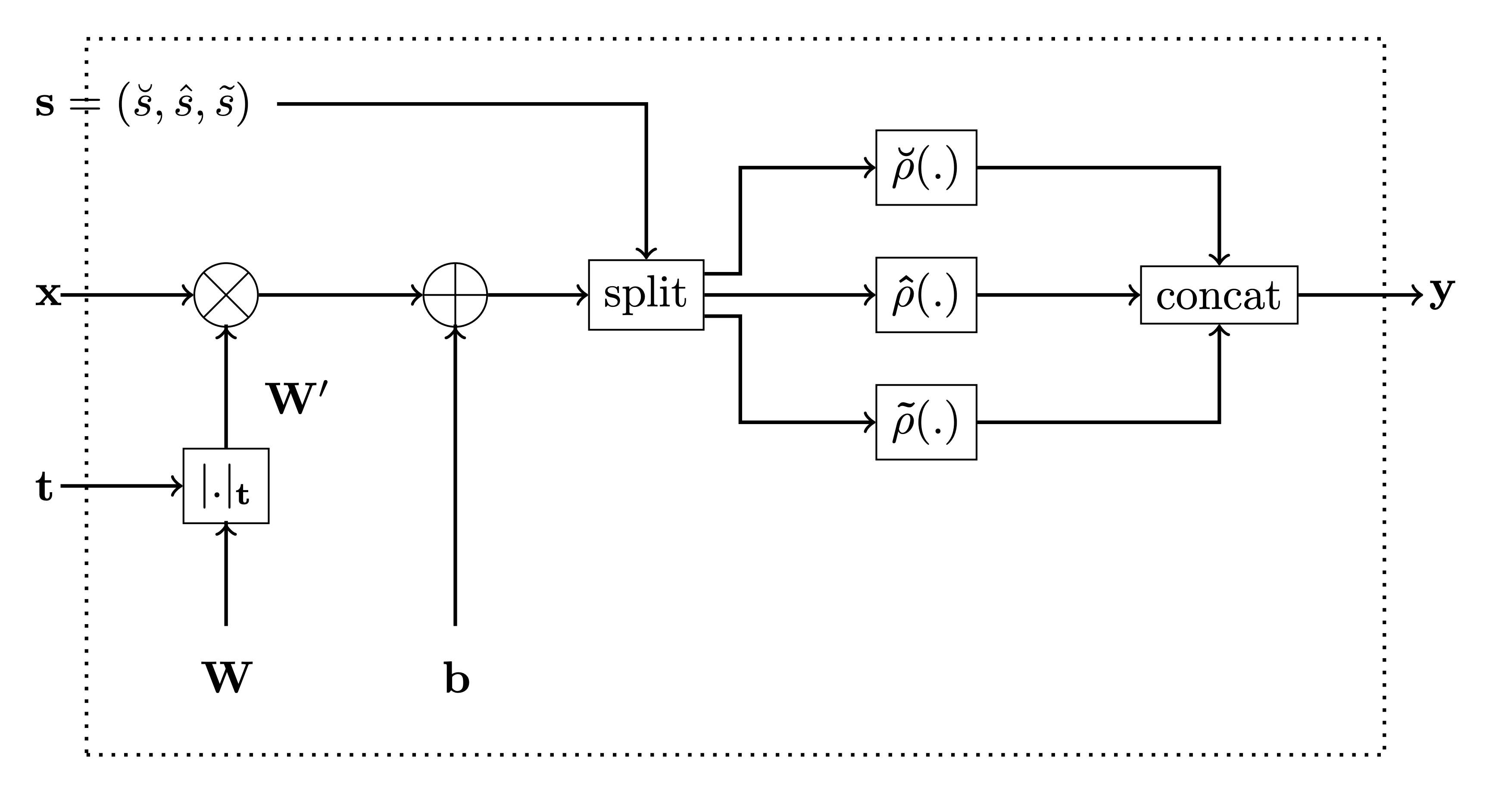
This is an implementation of our Monotonic Dense Unit or Constrained Monotone Fully Connected Layer. The below is the figure from the paper for reference.
-
the parameter
monotonicity_indicatorcorresponds to t in the figure below, and -
parameters
is_convex,is_concaveandactivation_weightsare used to calculate the activation selector s as follows:-
if
is_convexoris_concaveis True, then the activation selector s will be (units, 0, 0) and (0,units, 0), respecively. -
if both
is_convexoris_concaveis False, then theactivation_weightsrepresent ratios between \(\breve{s}\), \(\hat{s}\) and \(\tilde{s}\), respecively. E.g. ifactivation_weights = (2, 2, 1)andunits = 10, then
-
Source code in airt/_components/mono_dense_layer.py
181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 | |
Attributes¤
activation_weights = activation_weights
instance-attribute
¤
is_concave = is_concave
instance-attribute
¤
is_convex = is_convex
instance-attribute
¤
monotonicity_indicator = monotonicity_indicator
instance-attribute
¤
org_activation = activation
instance-attribute
¤
units = units
instance-attribute
¤
Functions¤
__init__(units: int, *, activation: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[TensorLike], TensorLike]]] = None, monotonicity_indicator: ArrayLike = 1, is_convex: bool = False, is_concave: bool = False, activation_weights: Tuple[float, float, float] = (7.0, 7.0, 2.0), **kwargs: Any)
¤
Constructs a new MonoDense instance.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
units |
int
|
Positive integer, dimensionality of the output space. |
required |
activation |
Optional[Union[str, Callable[[TensorLike], TensorLike]]]
|
Activation function to use, it is assumed to be convex monotonically increasing function such as "relu" or "elu" |
None
|
monotonicity_indicator |
ArrayLike
|
Vector to indicate which of the inputs are monotonically increasing or monotonically decreasing or non-monotonic. Has value 1 for monotonically increasing, -1 for monotonically decreasing and 0 for non-monotonic. |
1
|
is_convex |
bool
|
convex if set to True |
False
|
is_concave |
bool
|
concave if set to True |
False
|
activation_weights |
Tuple[float, float, float]
|
relative weights for each type of activation, the default is (1.0, 1.0, 1.0). Ignored if is_convex or is_concave is set to True |
(7.0, 7.0, 2.0)
|
**kwargs |
Any
|
passed as kwargs to the constructor of |
{}
|
Raise
ValueError: - if both is_concave and is_convex are set to True, or - if any component of activation_weights is negative or there is not exactly three components
Source code in airt/_components/mono_dense_layer.py
204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 | |
add_loss(losses, **kwargs)
¤
Add loss tensor(s), potentially dependent on layer inputs.
Some losses (for instance, activity regularization losses) may be
dependent on the inputs passed when calling a layer. Hence, when reusing
the same layer on different inputs a and b, some entries in
layer.losses may be dependent on a and some on b. This method
automatically keeps track of dependencies.
This method can be used inside a subclassed layer or model's call
function, in which case losses should be a Tensor or list of Tensors.
Example:
class MyLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def call(self, inputs):
self.add_loss(tf.abs(tf.reduce_mean(inputs)))
return inputs
The same code works in distributed training: the input to add_loss()
is treated like a regularization loss and averaged across replicas
by the training loop (both built-in Model.fit() and compliant custom
training loops).
The add_loss method can also be called directly on a Functional Model
during construction. In this case, any loss Tensors passed to this Model
must be symbolic and be able to be traced back to the model's Inputs.
These losses become part of the model's topology and are tracked in
get_config.
Example:
inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)(inputs)
outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
# Activity regularization.
model.add_loss(tf.abs(tf.reduce_mean(x)))
If this is not the case for your loss (if, for example, your loss
references a Variable of one of the model's layers), you can wrap your
loss in a zero-argument lambda. These losses are not tracked as part of
the model's topology since they can't be serialized.
Example:
inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
d = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)
x = d(inputs)
outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
# Weight regularization.
model.add_loss(lambda: tf.reduce_mean(d.kernel))
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
losses |
Loss tensor, or list/tuple of tensors. Rather than tensors, losses may also be zero-argument callables which create a loss tensor. |
required | |
**kwargs |
Used for backwards compatibility only. |
{}
|
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
1429 1430 1431 1432 1433 1434 1435 1436 1437 1438 1439 1440 1441 1442 1443 1444 1445 1446 1447 1448 1449 1450 1451 1452 1453 1454 1455 1456 1457 1458 1459 1460 1461 1462 1463 1464 1465 1466 1467 1468 1469 1470 1471 1472 1473 1474 1475 1476 1477 1478 1479 1480 1481 1482 1483 1484 1485 1486 1487 1488 1489 1490 1491 1492 1493 1494 1495 1496 1497 1498 1499 1500 1501 1502 1503 1504 1505 1506 1507 1508 1509 1510 1511 1512 1513 1514 1515 1516 1517 1518 1519 1520 1521 1522 1523 1524 1525 1526 1527 1528 1529 1530 1531 1532 1533 1534 1535 1536 1537 1538 1539 1540 1541 1542 1543 1544 1545 1546 1547 1548 1549 1550 1551 1552 1553 1554 | |
add_metric(value, name = None, **kwargs)
¤
Adds metric tensor to the layer.
This method can be used inside the call() method of a subclassed layer
or model.
class MyMetricLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(MyMetricLayer, self).__init__(name='my_metric_layer')
self.mean = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='metric_1')
def call(self, inputs):
self.add_metric(self.mean(inputs))
self.add_metric(tf.reduce_sum(inputs), name='metric_2')
return inputs
This method can also be called directly on a Functional Model during
construction. In this case, any tensor passed to this Model must
be symbolic and be able to be traced back to the model's Inputs. These
metrics become part of the model's topology and are tracked when you
save the model via save().
inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)(inputs)
outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
model.add_metric(math_ops.reduce_sum(x), name='metric_1')
Note: Calling add_metric() with the result of a metric object on a
Functional Model, as shown in the example below, is not supported. This
is because we cannot trace the metric result tensor back to the model's
inputs.
inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)(inputs)
outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
model.add_metric(tf.keras.metrics.Mean()(x), name='metric_1')
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
value |
Metric tensor. |
required | |
name |
String metric name. |
None
|
|
**kwargs |
Additional keyword arguments for backward compatibility.
Accepted values:
|
{}
|
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
1581 1582 1583 1584 1585 1586 1587 1588 1589 1590 1591 1592 1593 1594 1595 1596 1597 1598 1599 1600 1601 1602 1603 1604 1605 1606 1607 1608 1609 1610 1611 1612 1613 1614 1615 1616 1617 1618 1619 1620 1621 1622 1623 1624 1625 1626 1627 1628 1629 1630 1631 1632 1633 1634 1635 1636 1637 1638 1639 1640 1641 1642 1643 1644 1645 1646 1647 1648 1649 1650 1651 1652 1653 1654 1655 1656 1657 1658 1659 1660 1661 1662 1663 1664 1665 1666 1667 1668 1669 1670 1671 1672 1673 1674 1675 1676 1677 1678 1679 1680 1681 1682 1683 1684 1685 1686 1687 1688 1689 1690 1691 1692 1693 1694 1695 1696 1697 1698 1699 1700 1701 1702 1703 1704 1705 1706 1707 1708 1709 1710 1711 1712 1713 1714 | |
add_update(updates)
¤
Add update op(s), potentially dependent on layer inputs.
Weight updates (for instance, the updates of the moving mean and
variance in a BatchNormalization layer) may be dependent on the inputs
passed when calling a layer. Hence, when reusing the same layer on
different inputs a and b, some entries in layer.updates may be
dependent on a and some on b. This method automatically keeps track
of dependencies.
This call is ignored when eager execution is enabled (in that case, variable updates are run on the fly and thus do not need to be tracked for later execution).
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
updates |
Update op, or list/tuple of update ops, or zero-arg callable
that returns an update op. A zero-arg callable should be passed in
order to disable running the updates by setting |
required |
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
1716 1717 1718 1719 1720 1721 1722 1723 1724 1725 1726 1727 1728 1729 1730 1731 1732 1733 1734 1735 1736 1737 1738 1739 1740 1741 1742 1743 1744 1745 1746 | |
add_variable(*args, **kwargs)
¤
Deprecated, do NOT use! Alias for add_weight.
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
2283 2284 2285 2286 2287 2288 2289 2290 2291 2292 | |
add_weight(name = None, shape = None, dtype = None, initializer = None, regularizer = None, trainable = None, constraint = None, use_resource = None, synchronization = tf.VariableSynchronization.AUTO, aggregation = tf.VariableAggregation.NONE, **kwargs)
¤
Adds a new variable to the layer.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
name |
Variable name. |
None
|
|
shape |
Variable shape. Defaults to scalar if unspecified. |
None
|
|
dtype |
The type of the variable. Defaults to |
None
|
|
initializer |
Initializer instance (callable). |
None
|
|
regularizer |
Regularizer instance (callable). |
None
|
|
trainable |
Boolean, whether the variable should be part of the layer's
"trainable_variables" (e.g. variables, biases)
or "non_trainable_variables" (e.g. BatchNorm mean and variance).
Note that |
None
|
|
constraint |
Constraint instance (callable). |
None
|
|
use_resource |
Whether to use a |
None
|
|
synchronization |
Indicates when a distributed a variable will be
aggregated. Accepted values are constants defined in the class
|
tf.VariableSynchronization.AUTO
|
|
aggregation |
Indicates how a distributed variable will be aggregated.
Accepted values are constants defined in the class
|
tf.VariableAggregation.NONE
|
|
**kwargs |
Additional keyword arguments. Accepted values are |
{}
|
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
The variable created. |
Raises:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ValueError
|
When giving unsupported dtype and no initializer or when
trainable has been set to True with synchronization set as
|
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 692 693 694 695 696 697 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716 717 718 719 720 721 722 723 724 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 750 751 | |
build(input_shape: Tuple, *args: List[Any], **kwargs: Any) -> None
¤
Build
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
input_shape |
Tuple
|
input tensor |
required |
args |
List[Any]
|
positional arguments passed to Dense.build() |
()
|
kwargs |
Any
|
keyword arguments passed to Dense.build() |
{}
|
Source code in airt/_components/mono_dense_layer.py
276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 | |
call(inputs: TensorLike) -> TensorLike
¤
Call
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
inputs |
TensorLike
|
input tensor of shape (batch_size, ..., x_length) |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
TensorLike
|
N-D tensor with shape: |
Source code in airt/_components/mono_dense_layer.py
291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 | |
compute_mask(inputs, mask = None)
¤
Computes an output mask tensor.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
inputs |
Tensor or list of tensors. |
required | |
mask |
Tensor or list of tensors. |
None
|
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
None or a tensor (or list of tensors, one per output tensor of the layer). |
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
976 977 978 979 980 981 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 989 990 991 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 | |
compute_output_signature(input_signature)
¤
Compute the output tensor signature of the layer based on the inputs.
Unlike a TensorShape object, a TensorSpec object contains both shape
and dtype information for a tensor. This method allows layers to provide
output dtype information if it is different from the input dtype.
For any layer that doesn't implement this function,
the framework will fall back to use compute_output_shape, and will
assume that the output dtype matches the input dtype.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
input_signature |
Single TensorSpec or nested structure of TensorSpec objects, describing a candidate input for the layer. |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
Single TensorSpec or nested structure of TensorSpec objects, describing how the layer would transform the provided input. |
Raises:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
TypeError
|
If input_signature contains a non-TensorSpec object. |
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
931 932 933 934 935 936 937 938 939 940 941 942 943 944 945 946 947 948 949 950 951 952 953 954 955 956 957 958 959 960 961 962 963 964 965 966 967 968 969 970 971 972 973 974 | |
count_params()
¤
Count the total number of scalars composing the weights.
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
An integer count. |
Raises:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ValueError
|
if the layer isn't yet built (in which case its weights aren't yet defined). |
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
2146 2147 2148 2149 2150 2151 2152 2153 2154 2155 2156 2157 2158 2159 2160 2161 2162 2163 2164 2165 2166 2167 2168 | |
finalize_state()
¤
Finalizes the layers state after updating layer weights.
This function can be subclassed in a layer and will be called after updating a layer weights. It can be overridden to finalize any additional layer state after a weight update.
This function will be called after weights of a layer have been restored from a loaded model.
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
1885 1886 1887 1888 1889 1890 1891 1892 1893 1894 1895 1896 | |
get_config() -> Dict[str, Any]
¤
Get config is used for saving the model
Source code in airt/_components/mono_dense_layer.py
265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 | |
get_input_at(node_index)
¤
Retrieves the input tensor(s) of a layer at a given node.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
node_index |
Integer, index of the node
from which to retrieve the attribute.
E.g. |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
A tensor (or list of tensors if the layer has multiple inputs). |
Raises:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
RuntimeError
|
If called in Eager mode. |
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
2024 2025 2026 2027 2028 2029 2030 2031 2032 2033 2034 2035 2036 2037 2038 2039 2040 2041 2042 | |
get_input_mask_at(node_index)
¤
Retrieves the input mask tensor(s) of a layer at a given node.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
node_index |
Integer, index of the node
from which to retrieve the attribute.
E.g. |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
A mask tensor |
|
|
(or list of tensors if the layer has multiple inputs). |
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
1898 1899 1900 1901 1902 1903 1904 1905 1906 1907 1908 1909 1910 1911 1912 1913 1914 1915 1916 | |
get_input_shape_at(node_index)
¤
Retrieves the input shape(s) of a layer at a given node.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
node_index |
Integer, index of the node
from which to retrieve the attribute.
E.g. |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
A shape tuple |
|
|
(or list of shape tuples if the layer has multiple inputs). |
Raises:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
RuntimeError
|
If called in Eager mode. |
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
1982 1983 1984 1985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 | |
get_output_at(node_index)
¤
Retrieves the output tensor(s) of a layer at a given node.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
node_index |
Integer, index of the node
from which to retrieve the attribute.
E.g. |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
A tensor (or list of tensors if the layer has multiple outputs). |
Raises:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
RuntimeError
|
If called in Eager mode. |
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
2044 2045 2046 2047 2048 2049 2050 2051 2052 2053 2054 2055 2056 2057 2058 2059 2060 2061 2062 | |
get_output_mask_at(node_index)
¤
Retrieves the output mask tensor(s) of a layer at a given node.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
node_index |
Integer, index of the node
from which to retrieve the attribute.
E.g. |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
A mask tensor |
|
|
(or list of tensors if the layer has multiple outputs). |
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
1918 1919 1920 1921 1922 1923 1924 1925 1926 1927 1928 1929 1930 1931 1932 1933 1934 1935 1936 | |
get_output_shape_at(node_index)
¤
Retrieves the output shape(s) of a layer at a given node.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
node_index |
Integer, index of the node
from which to retrieve the attribute.
E.g. |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
A shape tuple |
|
|
(or list of shape tuples if the layer has multiple outputs). |
Raises:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
RuntimeError
|
If called in Eager mode. |
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 | |
get_weights()
¤
Returns the current weights of the layer, as NumPy arrays.
The weights of a layer represent the state of the layer. This function returns both trainable and non-trainable weight values associated with this layer as a list of NumPy arrays, which can in turn be used to load state into similarly parameterized layers.
For example, a Dense layer returns a list of two values: the kernel
matrix and the bias vector. These can be used to set the weights of
another Dense layer:
layer_a = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, ... kernel_initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1.)) a_out = layer_a(tf.convert_to_tensor([[1., 2., 3.]])) layer_a.get_weights() [array([[1.], [1.], [1.]], dtype=float32), array([0.], dtype=float32)] layer_b = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, ... kernel_initializer=tf.constant_initializer(2.)) b_out = layer_b(tf.convert_to_tensor([[10., 20., 30.]])) layer_b.get_weights() [array([[2.], [2.], [2.]], dtype=float32), array([0.], dtype=float32)] layer_b.set_weights(layer_a.get_weights()) layer_b.get_weights() [array([[1.], [1.], [1.]], dtype=float32), array([0.], dtype=float32)]
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
Weights values as a list of NumPy arrays. |
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
1841 1842 1843 1844 1845 1846 1847 1848 1849 1850 1851 1852 1853 1854 1855 1856 1857 1858 1859 1860 1861 1862 1863 1864 1865 1866 1867 1868 1869 1870 1871 1872 1873 1874 1875 1876 1877 1878 1879 1880 1881 1882 1883 | |
set_weights(weights)
¤
Sets the weights of the layer, from NumPy arrays.
The weights of a layer represent the state of the layer. This function sets the weight values from numpy arrays. The weight values should be passed in the order they are created by the layer. Note that the layer's weights must be instantiated before calling this function, by calling the layer.
For example, a Dense layer returns a list of two values: the kernel
matrix and the bias vector. These can be used to set the weights of
another Dense layer:
layer_a = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, ... kernel_initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1.)) a_out = layer_a(tf.convert_to_tensor([[1., 2., 3.]])) layer_a.get_weights() [array([[1.], [1.], [1.]], dtype=float32), array([0.], dtype=float32)] layer_b = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, ... kernel_initializer=tf.constant_initializer(2.)) b_out = layer_b(tf.convert_to_tensor([[10., 20., 30.]])) layer_b.get_weights() [array([[2.], [2.], [2.]], dtype=float32), array([0.], dtype=float32)] layer_b.set_weights(layer_a.get_weights()) layer_b.get_weights() [array([[1.], [1.], [1.]], dtype=float32), array([0.], dtype=float32)]
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
weights |
a list of NumPy arrays. The number
of arrays and their shape must match
number of the dimensions of the weights
of the layer (i.e. it should match the
output of |
required |
Raises:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ValueError
|
If the provided weights list does not match the layer's specifications. |
Source code in /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.9.17/x64/lib/python3.9/site-packages/keras/engine/base_layer.py
1748 1749 1750 1751 1752 1753 1754 1755 1756 1757 1758 1759 1760 1761 1762 1763 1764 1765 1766 1767 1768 1769 1770 1771 1772 1773 1774 1775 1776 1777 1778 1779 1780 1781 1782 1783 1784 1785 1786 1787 1788 1789 1790 1791 1792 1793 1794 1795 1796 1797 1798 1799 1800 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 1807 1808 1809 1810 1811 1812 1813 1814 1815 1816 1817 1818 1819 1820 1821 1822 1823 1824 1825 1826 1827 1828 1829 1830 1831 1832 1833 1834 1835 1836 1837 1838 1839 | |